The ASTM E-84 is the standard test method for assessing the surface burning characteristics of building products. The purpose of this test is to observe the flame spread along a prepared sample in order to determine the relative burning behavior of the tested material. The ASTM E-84 test measures both the Flame Spread Index (FSI) and Smoke Developed Index (SDI). FSI is the measurement for the speed at which flames progress across the interior surface of a building, while SDI measures the amount of smoke a sample emits as it burns.
The International Building Code (IBC) specifies that interior wall and ceiling finishes shall be classified in accordance with ASTM E84 (Table 1). Additionally, the National Fire Protection Agency (NFPA) 101 Life Safety Code requires that an interior wall or ceiling finish to be Class A, Class B, or Class C based on test results from ASTM E-84 (NFPA 255 or UL 723). Class A is the highest rated system and Class C is the lowest rated system. Most interior applications require Class A rated products. Class A rated products can be used in areas of the building that require Class B or C products, however, you cannot use Class C or Class B rated products in Class A required areas.
TABLE 1 – Class Ratings for ASTM E-84
| Class Rating Designations | Flame Spread Index (FSI) | Smoke Development Index (SDI) |
| Class A | 0-25 | 450 max |
| Class B | 26-75 | 450 max |
| Class C | 76-200 | 450 max |
An ASTM E-84 test is conducted by placing a 24” wide x 24’ long sample into a Steiner Tunnel Testing Assembly (see photo below), where the test is administered through the use of two burners which provide 89kW of energy. During the test, the sample is mounted under a removable lid and a forced draft is provided in order for the movement of air and products of combustion within the tunnel. The progress of the flame is then monitored through viewports on one side of the apparatus and recorded, with software computing the various data points to derive the FSI and SDI. Smoke developed is also measured through the optical density of a light obscuration meter.
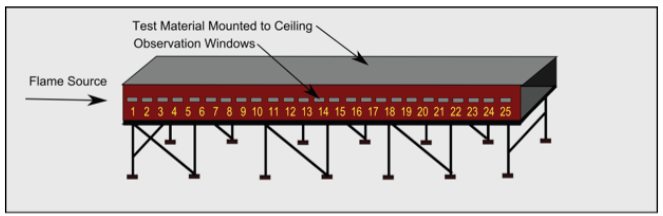
Steiner Tunnel (ASTM E-84) Testing Assembly
A polymeric coating incorporating NeoGraf Solutions’ GrafGuard® expandable graphite can be applied to a suitable substrate to be evaluated. The substrate could be wood, metal or a variety of other composite materials.
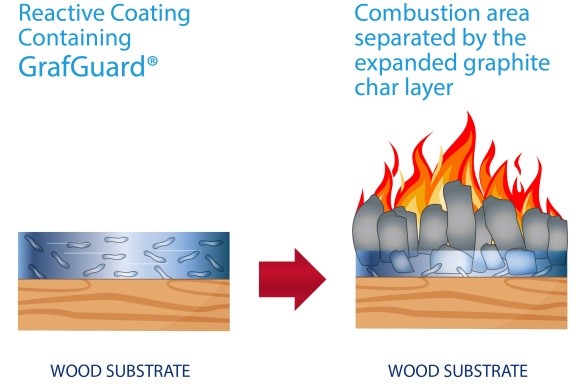
Figure 1
The GrafGuard flakes expand into a charred intumescent foam when exposed to the heat of the fire (Figure 1). The charred intumescent foam protects and insulates the base polymer from the fire. GrafGuard systems can expand up to 300X and the wind driven draft nature of the test must be taken into consideration. The charred intumescent GrafGuard foam can be densified utilizing a variety of synergistic chemical intumescent products. This densified char can withstand the wind driven force and protect the base polymer from exposure to the heat of the fire. Minimizing both the smoke development and flame spread maximizes the potential flame spread index classification of the base polymer material. This allows manufacturers using GrafGuard graphite flake to utilize their products for more diverse applications in the field yielding increased sales.
# # # #
James Derrigan
Regional Sales Manager – NeoGraf Solutions

